Nitrogen: DAMNED IF YOU DO, DAMNED IF YOU DON'T
Nitrogen fertilizers are an important tool for many farmers, but overuse is a serious threat to the environment.
NITROGEN OVERUSE
Nitrogen is one of six macronutrients essential plant growth. In the middle of the 20th century, application of nitrogen-containing fertilizers was one of several advances in agricultural technology that resulted in increased agricultural production worldwide.
This increase in production allowed agricultural production to keep pace with population growth and is estimated to have prevented starvation on a broad scale.
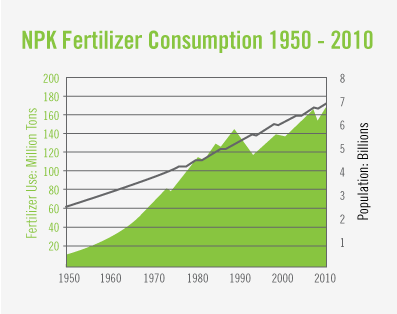
According to the International Fertilizer Association, use of fertilizers containing nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium grew from 14 million metric tons in 1950 to more than 177 million metric tons in 2011.
The use of nitrogen fertilizers comes at a cost. Excess nitrogen can:
- runoff into surface water,
- infiltrate into groundwater, or
- be released into the atmosphere as nitrous oxide.
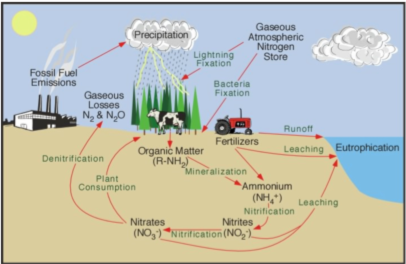
Excess levels of nitrogen in surface water cause eutrophication, a proliferation of algae and other plant life that causes fish and marine animals to die off due to a lack of oxygen. Infiltration of nitrogen into groundwater causes nitrate contamination of shallow drinking water sources. When emitted to the atmosphere, nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas. According to the EPA, each molecule has 310 times the global warming potential of a molecule of carbon dioxide.
Getting It Just Right
The Earth Restoration Foundation’s mission is to lead the advancement of global soil science and education. We work for a future where farmers worldwide have the knowledge to apply the type and amount of fertilizers and soil amendments that will produce high yields while minimizing detrimental impacts on the environment.